Homeostasis Concept Map
Summary
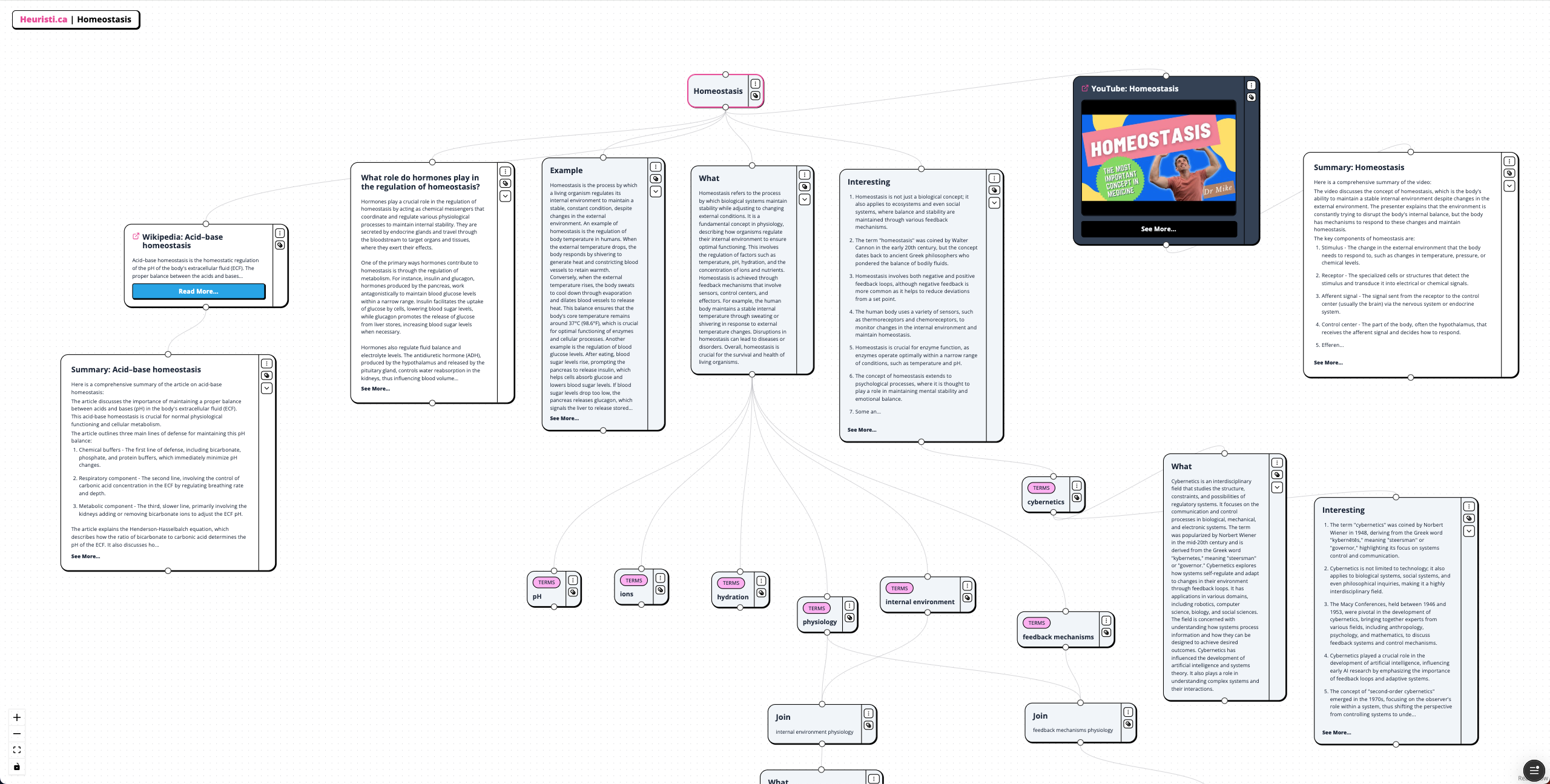
Homeostasis is the process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions. It is essential for the survival and health of living organisms, involving the regulation of factors such as temperature, pH, hydration, and the concentration of ions and nutrients. Feedback mechanisms, including sensors, control centers, and effectors, play a crucial role in achieving homeostasis. For instance, the human body regulates its internal temperature through sweating or shivering in response to external temperature changes.
The study of internal environment physiology focuses on how various physiological systems, such as the circulatory, respiratory, and nervous systems, work together to maintain homeostasis. Disruptions in these systems can lead to diseases or disorders. Feedback mechanisms are categorized into negative feedback, which counteracts changes to restore balance, and positive feedback, which amplifies changes to drive processes to completion, such as during childbirth.
Oxytocin, a hormone produced in the hypothalamus, plays a significant role in social bonding and reproduction, particularly during childbirth. The hypothalamus itself is crucial for maintaining homeostasis by regulating various physiological processes, including temperature, hunger, and emotional responses. Circadian rhythms, which regulate the sleep-wake cycle, are also influenced by the hypothalamus and are essential for overall health.
The nervous system, divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), coordinates bodily functions and responses to external stimuli. The CNS processes information and controls most body functions, while the PNS connects the CNS to limbs and organs, facilitating communication throughout the body.
Cybernetics, an interdisciplinary field, studies regulatory systems and feedback processes in biological and mechanical systems. It has applications in various domains, including artificial intelligence and systems theory, and emphasizes the importance of feedback loops in maintaining stability and control.
Overall, the mechanisms of homeostasis are vital for maintaining a stable internal environment, adapting to changes, and ensuring optimal functioning of biological systems.
Key Takeaways
- It involves the regulation of factors such as temperature, pH, hydration, and ion concentration.
- Feedback mechanisms, including sensors, control centers, and effectors, are essential for achieving homeostasis.
- Disruptions in homeostasis can lead to diseases or disorders.
- The internal environment physiology studies the conditions necessary for maintaining life within organisms.
- Feedback mechanisms are categorized into negative feedback, which counteracts changes, and positive feedback, which amplifies changes.
- Oxytocin is a hormone involved in social bonding, reproduction, and childbirth, produced in the hypothalamus.
- The hypothalamus regulates various physiological processes, including temperature, hunger, and emotional responses.
- Circadian rhythms are internal processes that regulate the sleep-wake cycle and are influenced by external cues.
- The nervous system coordinates actions and transmits signals between the brain and body, playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis.
- The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to limbs and organs, facilitating communication and response to stimuli.
- The central nervous system processes and transmits information, controlling most bodily functions and responses.
- Hormones act as chemical messengers that regulate physiological processes to maintain internal stability.
- Acid-base homeostasis is vital for normal physiological functioning, involving chemical buffers, respiratory control, and metabolic adjustments.
- Cybernetics studies regulatory systems and feedback processes in biological and mechanical systems, influencing various fields including AI and systems theory.
Additional Concepts
Questions and Answers
What is homeostasis?
What role do hormones play in homeostasis?
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
What are feedback mechanisms in physiology?
What is the peripheral nervous system?
What is cybernetics?
What is the significance of circadian rhythms?
Flashcards
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis refers to the process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions, ensuring optimal functioning of organisms.
What role do feedback mechanisms play in homeostasis?
Feedback mechanisms help maintain homeostasis by regulating internal conditions, primarily through negative feedback, which counteracts changes, and positive feedback, which amplifies changes.
What is the function of the hypothalamus in homeostasis?
The hypothalamus regulates various physiological processes, including temperature, hunger, thirst, and emotional responses, and controls the autonomic and endocrine systems to maintain homeostasis.
How do hormones contribute to homeostasis?
Hormones act as chemical messengers that coordinate and regulate physiological processes, such as metabolism, fluid balance, and the stress response, to maintain internal stability.
What are circadian rhythms?
Circadian rhythms are natural, internal processes that regulate the sleep-wake cycle and other bodily functions, repeating roughly every 24 hours and influenced by external cues like light.
What is the central nervous system (CNS)?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and transmitting information throughout the body, controlling most bodily functions and responses.
What is the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
The peripheral nervous system includes all nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord, connecting the CNS to limbs and organs, and facilitating communication between the brain and the body.
What is oxytocin and its role in the body?
Oxytocin is a hormone involved in social bonding, reproduction, and childbirth, playing a crucial role in uterine contractions during labor and influencing behaviors like trust and empathy.
What are the three main lines of defense for acid-base homeostasis?
The three main lines of defense for acid-base homeostasis are chemical buffers, the respiratory component regulating breathing, and the metabolic component involving the kidneys.